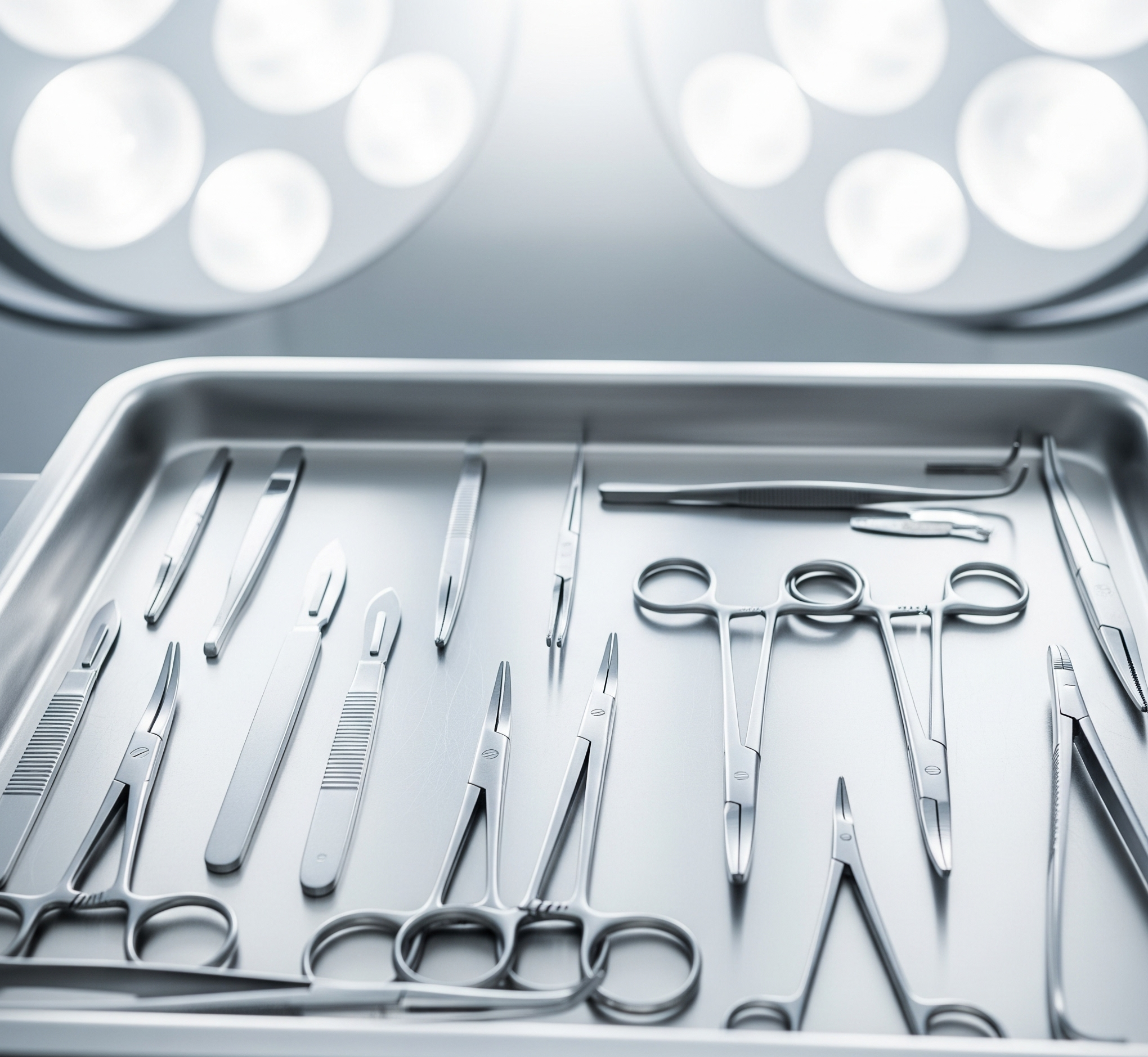
Introduction
In surgery, precision can mean the difference between life and death. Surgeons and healthcare professionals depend on specialized tools, each crafted for a specific task. But for learners, practitioners, and researchers, surgical instruments pictures are equally important. Visual learning enhances recognition, speeds up training, and helps avoid errors in real-life procedures.
From scalpels and forceps to powered orthopedic drills, pictures of surgical instruments provide clarity on design, function, and application. In this article, we will explore the importance of surgical instruments pictures, their categories, historical evolution, and how images are shaping modern medical education.
Importance of Surgical Instruments Pictures
Why do pictures matter in the study of surgical tools?
- Identification: Pictures help differentiate between similar-looking instruments.
- Education: Students and nurses memorize instrument names and functions more easily.
- Training: Visual references prepare learners before handling real tools.
- Reference: Catalogs use images so buyers know exactly what they are purchasing.
- History: Museums display instrument pictures to preserve medical heritage.
In short, surgical instruments pictures act as a bridge between theory and practice.
Major Categories of Surgical Instruments (with Picture Relevance)
Surgical instruments can be divided into categories. Pictures make these classifications easier to understand.
1. Cutting and Dissecting Instruments
- Scalpels: Sharp blades for precise incisions.
- Surgical Scissors: Curved or straight scissors for tissue or sutures.
- Bone Saws: For orthopedic operations and amputations.
2. Grasping and Holding Instruments
- Tissue Forceps: Tweezer-like tools for gripping soft tissues.
- Needle Holders: Essential for stitching wounds.
- Towel Clamps: Used to secure drapes during surgery.
3. Clamping and Occluding Instruments
- Hemostats: Control bleeding by clamping blood vessels.
- Artery Forceps: For vascular control.
- Bulldog Clamps: Apply gentle pressure to arteries or veins.
4. Retracting and Exposing Instruments
- Retractors: Pull back tissues to expose the surgical site.
- Hooks: Used in plastic and general surgeries.
- Speculums: Used in gynecology to view cavities.
5. Suction and Aspiration Instruments
- Yankauer Suction: Removes blood and fluids.
- Frazier Suction Tip: Used in delicate neurosurgery.
- Catheters: Assist in fluid removal.
6. Probing and Dilating Instruments
- Probes: Explore wounds and apply treatments.
- Dilators: Widen passages such as the cervix or urethra.
- Sounds: Measure and probe cavities.
7. Suturing and Stapling Instruments
- Needle Holders: Grip needles during suturing.
- Surgical Staplers: Quick closure of incisions.
- Ligature Carriers: Place sutures in deep tissues.
8. Powered and Advanced Instruments
- Drills and Reamers: Orthopedic bone surgeries.
- Dermatomes: For harvesting skin grafts.
- Endoscopic Tools: Used in minimally invasive procedures.
📸 Pictures of each of these categories make it easier for learners to distinguish their designs.
Surgical Instruments Pictures in Education
Pictures are heavily used in:
- Medical Textbooks: Include detailed diagrams and labeled images.
- Nursing and MBBS Exams: Students identify instruments from pictures.
- Virtual Training: Online platforms provide interactive image-based quizzes.
- Hospital Catalogs: Display high-quality product images.
Without pictures, medical training would be incomplete.
Where to Access Surgical Instruments Pictures
- Textbooks and Atlases: Classic resources for students.
- University Websites: Offer free libraries of labeled pictures.
- Manufacturers’ Catalogs: Suppliers publish images for buyers.
- Medical Blogs: Provide instrument picture guides.
- Museums and Archives: Display ancient and medieval surgical tools.
Historical Perspective of Surgical Instrument Pictures
Pictures also preserve history. Ancient tools discovered in Egypt, Greece, and Rome show how advanced early medicine was. For instance:
- Roman Speculums look almost identical to modern ones.
- Bone Drills from ancient times resemble orthopedic drills today.
- Forceps existed centuries ago and continue to evolve.
By studying these pictures, one can trace the journey of surgical innovation.
Role of Modern Technology in Surgical Instrument Imaging
Today’s education uses advanced visualization techniques:
- 3D Models: Rotate instruments for better understanding.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Students interact with lifelike images.
- Digital Catalogs: Offer downloadable PDFs with pictures.
- Mobile Apps: Provide quick reference with labeled photos.
This has transformed medical training into an accessible, interactive experience.
Benefits of Surgical Instruments Pictures
- Boosts Memory Retention: Visuals make names and functions easier to remember.
- Reduces Errors: Differentiates between similar tools.
- Accessible Learning: Global students can learn online.
- Cross-Specialty Recognition: Helps professionals outside their field understand instruments.
Conclusion
Surgical instruments pictures are not just illustrations—they are essential educational and professional tools. By visually categorizing instruments, pictures provide clarity for students, surgeons, suppliers, and patients alike.
From scalpels and scissors to powered orthopedic drills, pictures make medical learning more effective. Historical images remind us of medicine’s evolution, while modern digital resources take education to the next level.
At Professional Enterprises, we provide high-quality surgical and dental instruments crafted from German stainless steel. Our product catalogs include clear pictures, ensuring healthcare professionals can easily identify and select the right tools for their practice.