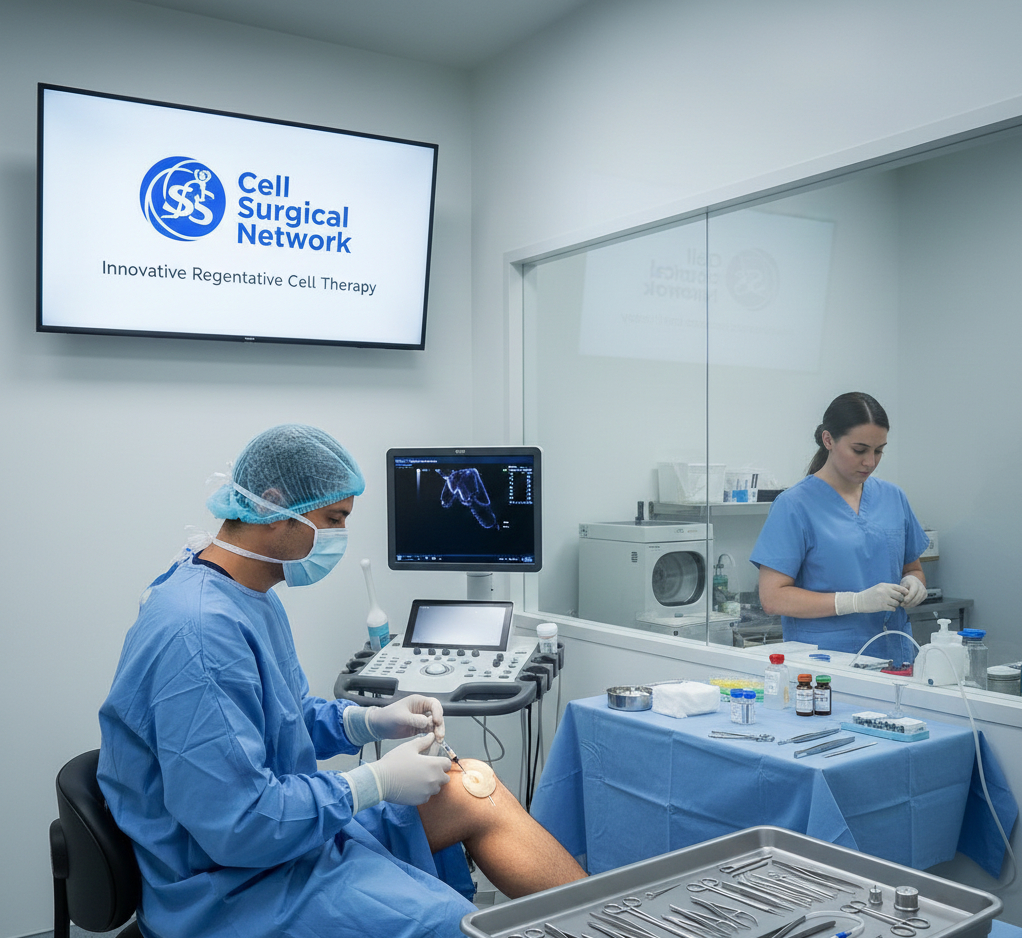
Introduction
The field of regenerative medicine is rapidly evolving, with an increasing focus on cellular therapies that harness the body’s own healing potential. One organization at the forefront of this movement is the Cell Surgical Network—a collaborative group of medical professionals, researchers, and clinics dedicated to advancing the use of regenerative cellular therapies for a wide range of conditions.
As interest grows in treatments like stem cell therapy, PRP (platelet-rich plasma), and advanced tissue repair, many patients and practitioners are asking: What is the Cell Surgical Network? How do its therapies work? Are these treatments safe and effective? This comprehensive article answers these questions with clear, evidence-based information, organized for easy reading and strong SEO relevance.
We’ll cover the history of the network, its mission, the therapies offered, scientific principles, patient outcomes, regulatory context, benefits, risks, and future innovations in regenerative medicine.
What Is the Cell Surgical Network?
Cell Surgical Network (CSN) is a network of affiliated medical practices and providers specializing in regenerative cellular therapies. These therapies are designed to leverage the biological power of cells—often derived from the patient—to promote healing, reduce inflammation, and support tissue regeneration across various medical and orthopedic conditions.
While many regenerative therapies are still under clinical study, the network aims to deliver cutting-edge care while emphasizing safety, ethical responsibility, and scientific rigor.
The mission of the Cell Surgical Network includes:
- Advancing regenerative medicine approaches
- Enabling collaboration between providers
- Educating patients and providers about cellular therapies
- Developing and refining treatment protocols
The Science Behind Regenerative Cell Therapies
Stem Cells and Regeneration
At the core of many regenerative therapies offered through the Cell Surgical Network are stem cells—undifferentiated cells with the potential to become various specialized cell types and support tissue repair.
Common sources for cells used in CSN protocols include:
- Adipose-derived (fat) stem cells
- Bone marrow cells
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP)
These cells are thought to:
- Reduce inflammation
- Promote angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation)
- Release growth factors
- Support tissue remodeling
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
Platelet-rich plasma is obtained from the patient’s blood and concentrated to enhance its therapeutic properties. PRP is rich in growth factors that may support healing in joints, tendons, and soft tissues.
Cell Processing and Quality
The Cell Surgical Network emphasizes:
- Sterile processing
- Minimally manipulated cells
- Adherence to safety protocols
- Use of high-quality laboratory techniques
Note that “minimally manipulated” refers to cell preparation that complies with certain regulatory definitions, impacting how therapies are categorized under safety and oversight guidelines.
Common Conditions Treated Through CSN Clinics
The regenerative therapies facilitated through the Cell Surgical Network are used for a variety of orthopaedic, autoimmune, and degenerative conditions, including but not limited to:
Orthopedic and Musculoskeletal Conditions
- Osteoarthritis of knee, hip, shoulder
- Tendinopathies (e.g., Achilles, rotator cuff)
- Ligament injuries
- Cartilage degeneration
- Back and disc pain
Autoimmune and Inflammatory Disorders
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus-related joint pain
- Chronic inflammatory conditions
Other Applications Under Investigation
- Wound healing
- Soft tissue injuries
- Some dermatologic uses
- Potential chronic pain applications
While these therapies are promising, it’s important to acknowledge that outcomes vary and clinical evidence is still evolving for many of these indications.
How Cell Surgical Network Treatments Are Administered
Patient Evaluation
- Detailed medical history
- Physical examination
- Imaging (MRI, X-ray, ultrasound as needed)
- Laboratory work if indicated
A customized treatment plan is created based on the patient’s individual condition.
Procedure Overview
- Cell or PRP Harvest
- Adipose tissue or blood is collected from the patient
- Processing
- Cells are concentrated and prepared under sterile conditions
- Targeted Delivery
- Injection under ultrasound or fluoroscopic guidance
- Post-Procedure Care
- Activity modification
- Follow-up monitoring
The use of imaging guidance ensures accurate placement of cells into the affected tissues.
Outcomes and Patient Experiences
Many patients report:
- Reduced pain
- Improved function
- Increased mobility
- Delayed need for surgical intervention
However, results vary based on:
- Severity of condition
- Patient age and health
- Type of therapy used
- Precise technique and delivery
It’s important for patients to have realistic expectations and understand that regenerative treatments may not be a “cure” but rather part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Safety and Risks
Reported Side Effects
- Mild swelling or soreness at injection site
- Temporary discomfort
- Rare allergic or inflammatory response
Safety Measures
Cell Surgical Network providers follow strict protocols for:
- Sterility
- Patient screening
- Qualified delivery techniques
- Follow-up monitoring
Though complications are uncommon, patients should discuss potential risks with their provider.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Regenerative therapies reside in a complex regulatory environment. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates human cells, tissues, and cellular and tissue-based products (HCT/Ps). Some regenerative treatments operate within regulatory frameworks that define “minimal manipulation” and “homologous use.”
Patients considering Cell Surgical Network therapies should:
- Verify clinic compliance
- Ask about tissue source and processing
- Understand whether treatment is investigational
- Know consent expectations
Education and transparency help patients make informed decisions.
Cell Surgical Network vs Traditional Surgery
Advantages of Regenerative Approaches
| Regenerative Therapy | Traditional Surgery |
|---|---|
| Minimally invasive | Major surgery |
| Short recovery time | Longer rehabilitation |
| Uses patient’s own cells | Requires implants/prosthetics |
| Less pain risk | Higher surgical risk |
Regenerative therapy is often pursued when surgery is not yet necessary or when patients seek alternatives to invasive procedures.
Scientific Research and Clinical Studies
The landscape of regenerative medicine continues to expand, with ongoing research in:
- Stem cell tracking
- Growth factor optimization
- Long-term outcome studies
- Combined biologic therapies
Cell Surgical Network clinics may participate in registries and collaborative data collection to improve outcomes and contribute to scientific literature.
Patient Selection: Who Is a Candidate?
Not all patients are ideal candidates for regenerative cellular therapies.
Good Candidates Tend To Be:
- Mild to moderate degenerative conditions
- Failure of conservative therapy
- Desire to avoid or delay surgery
- Generally healthy without severe comorbidities
Patients with advanced joint collapse, active infection, or significant systemic disease may require alternative interventions.
Preparing for Treatment
Before undergoing regenerative therapy through a Cell Surgical Network clinic, patients should:
- Review medical history thoroughly
- Discuss realistic goals
- Understand costs (often not covered by insurance)
- Arrange for post-procedure support
Pre-procedure readiness often impacts overall experience and outcomes.
Cost Considerations
- Regenerative therapy costs vary widely
- Typically not fully covered by insurance
- May range from several hundred to several thousand dollars depending on:
- Type of therapy (PRP vs cellular)
- Number of treatments
- Location and provider expertise
Patients should receive transparent pricing and options for financing when available.
Comparing Cell Surgical Network to Other Providers
When comparing Cell Surgical Network to other regenerative therapy providers:
Consider:
- Provider experience and credentials
- Volume of treated cases
- Use of imaging guidance (ultrasound/fluoroscopy)
- Follow-up support and success reporting
Reviews, testimonials, and referrals from trusted clinicians can help guide decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Cell Surgical Network a hospital?
No—Cell Surgical Network is a group of affiliated clinics and physicians offering regenerative cell therapy, not a single hospital facility.
Are these treatments FDA-approved?
Some components of regenerative therapy fall under FDA guidelines for HCT/Ps. However, many treatments are considered investigational and not formally FDA-approved indications.
What conditions can be treated?
Commonly treated conditions include orthopedic pain, tendon injuries, arthritis pain, and soft tissue degeneration.
How long do results last?
Outcomes vary. Some patients experience long-term relief, while others may require follow-up treatments.
Is the therapy painful?
Procedures are usually minimally painful, often performed under local anesthesia with minimal downtime.
Future of Regenerative Medicine and CSN
The future of regenerative therapy and networks like Cell Surgical Network includes:
- Enhanced stem cell quality metrics
- Predictive outcome modeling
- Personalized biologics
- Combination therapies (PRP + cells + scaffolds)
- Improved clinical evidence
As research grows, so will patient confidence and treatment precision.
Conclusion
The Cell Surgical Network represents a significant chapter in the story of regenerative medicine, offering patients alternative paths to healing through cellular therapies. While outcomes depend on many factors, advancements in science and clinical practice continue to improve patient care. Understanding the mission, therapies, risks, and benefits of this network helps patients and providers make informed decisions aligned with modern medical standards.