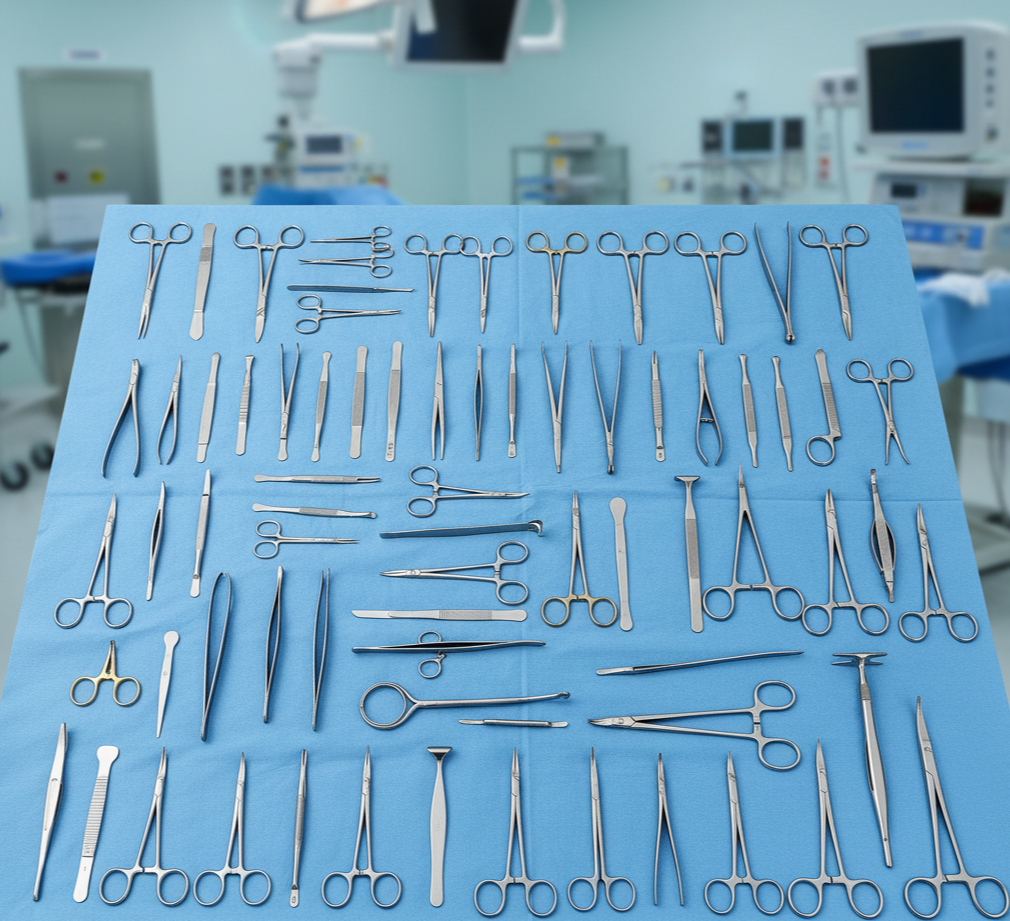
Surgical instruments are the foundation of every successful operation. From simple wound suturing to complex organ transplants, precision tools are essential. Knowing the 54 basic surgical instruments with pictures helps medical students, nurses, and professionals identify each instrument quickly and understand its function.
In this complete guide, we’ll list the most commonly used surgical instruments by category — including their names, functions, and picture descriptions for better understanding.
Why Learn 54 Basic Surgical Instruments with Pictures
Learning surgical instruments visually enhances knowledge and accuracy during real procedures. Here’s why it’s important:
- ✅ Improves Recognition: Photos make it easier to identify instruments in practice.
- ✅ Boosts Confidence: Professionals can handle the right instrument without confusion.
- ✅ Supports Training: Visual learning benefits medical students and nurses.
- ✅ Assists Buyers: Helps in selecting correct products for hospitals and clinics.
Categories of 54 Basic Surgical Instruments with Pictures
Surgical instruments are classified into functional categories such as cutting, clamping, grasping, retracting, suturing, and specialized tools.
Let’s explore each category with names and image descriptions.
1. Cutting and Dissecting Instruments
These are used to cut tissue, skin, sutures, and materials during surgery.
1. Scalpel Handle and Blades
- Use: For making precise surgical incisions.
- Picture Description: Stainless steel handle with detachable sharp blade.
2. Surgical Scissors (Straight and Curved)
- Use: For cutting tissue and sutures.
- Picture Description: Pair of stainless scissors with sharp, pointed ends.
3. Metzenbaum Scissors
- Use: Fine dissection of delicate tissue.
- Picture Description: Curved slender scissors with smooth blades.
4. Mayo Scissors
- Use: To cut thick tissues or sutures.
- Picture Description: Heavy scissors with strong blades.
5. Bone Cutter
- Use: Cuts bones in orthopedic procedures.
- Picture Description: Heavy-duty plier-style tool.
6. Osteotome
- Use: Chiseling or cutting bone.
- Picture Description: Flat chisel with beveled edges.
7. Tenotomy Scissors
- Use: Fine tissue dissection in ophthalmic surgery.
- Picture Description: Slim scissors with sharp tips.
8. Amputation Knife
- Use: For large cuts during limb amputation.
- Picture Description: Long handle knife with wide blade.
2. Grasping and Holding Instruments
These are used to hold tissues, organs, or surgical materials firmly.
9. Tissue Forceps
- Use: For grasping soft tissues.
- Picture Description: Tweezer-like instrument with toothed tips.
10. Dressing Forceps
- Use: Holds gauze or dressing materials.
- Picture Description: Long forceps with serrated jaws.
11. Adson Forceps
- Use: For fine tissue handling in plastic or general surgery.
- Picture Description: Small forceps with delicate teeth.
12. Allis Tissue Forceps
- Use: To grasp tough tissue like fascia.
- Picture Description: Ring handle forceps with interlocking teeth.
13. Babcock Forceps
- Use: Holds delicate tissue like intestines.
- Picture Description: Smooth rounded jaws.
14. Sponge Forceps
- Use: Holds sponges for cleaning surgical sites.
- Picture Description: Circular tip with ring handles.
15. Towel Clamp
- Use: Holds surgical drapes.
- Picture Description: Pointed curved ends with locking handle.
16. Needle Holder
- Use: Grips suturing needle firmly.
- Picture Description: Short jaws with cross-hatched pattern.
3. Clamping and Occluding Instruments
These are designed to control bleeding and clamp blood vessels.
17. Hemostat (Artery Forceps)
- Use: To clamp small vessels.
- Picture Description: Curved or straight jaws with ratchet lock.
18. Kelly Clamp
- Use: Larger vessel clamping.
- Picture Description: Medium-length handle and serrated jaws.
19. Mosquito Clamp
- Use: For small delicate vessels.
- Picture Description: Fine curved tips, small size.
20. Crile Forceps
- Use: To clamp blood vessels.
- Picture Description: Straight hemostat with full serrations.
21. Kocher Forceps
- Use: Grips tissue firmly with teeth.
- Picture Description: Straight clamp with interlocking tooth.
22. Bulldog Clamp
- Use: Temporary vascular occlusion.
- Picture Description: Small, spring-loaded clamp.
23. Right Angle Clamp (Mixter)
- Use: Clamping in deep surgical areas.
- Picture Description: 90-degree angled tip.
4. Retracting and Exposing Instruments
These instruments hold back tissues for clear visibility.
24. Handheld Retractor
- Use: Exposes wound or cavity.
- Picture Description: Smooth curved blade with handle.
25. Self-Retaining Retractor
- Use: Holds tissue automatically.
- Picture Description: Retractor with ratchet locking mechanism.
26. Senn Retractor
- Use: For small incisions or soft tissue surgeries.
- Picture Description: Double-ended hook retractor.
27. Deaver Retractor
- Use: Retracts deep abdominal tissue.
- Picture Description: Broad curved blade.
28. Richardson Retractor
- Use: Retracts abdominal wall.
- Picture Description: L-shaped stainless retractor.
29. Balfour Retractor
- Use: Keeps abdominal incision open.
- Picture Description: Large self-retaining frame retractor.
30. Skin Hook
- Use: Retracts delicate skin.
- Picture Description: Slender handle with small hook tip.
31. Vaginal Speculum
- Use: Opens vaginal cavity for examination.
- Picture Description: Two-blade stainless device.
5. Suturing and Stapling Instruments
Used for wound closure and tissue approximation.
32. Mayo-Hegar Needle Holder
- Use: For suturing and needle holding.
- Picture Description: Cross-hatched jaws with locking handle.
33. Olsen-Hegar Needle Holder
- Use: Combines needle holder and scissors.
- Picture Description: Short jaw with cutting blade near hinge.
34. Lister Suture Scissors
- Use: Cuts sutures neatly.
- Picture Description: Small angled scissors.
35. Surgical Stapler
- Use: Closes incisions quickly.
- Picture Description: Disposable handheld stapler.
36. Suture Removal Scissors
- Use: Removes stitches.
- Picture Description: Hooked blade tip.
6. Orthopedic Surgical Instruments
Used for bone and joint surgeries.
37. Bone Drill
- Use: Drills holes for screws and plates.
- Picture Description: Manual or powered drill.
38. Bone Saw
- Use: Cuts bones.
- Picture Description: Gigli wire or oscillating saw.
39. Bone File
- Use: Smooths bone edges.
- Picture Description: Serrated metal file.
40. Chisel and Mallet
- Use: Bone cutting and shaping.
- Picture Description: Flat chisel with hammer.
7. Dental Surgical Instruments
41. Extraction Forceps
- Use: Removes teeth.
- Picture Description: Stainless steel plier with curved beak.
42. Elevator
- Use: Loosens tooth before extraction.
- Picture Description: Curved tip with ergonomic handle.
43. Scaler
- Use: Removes plaque and calculus.
- Picture Description: Fine pointed instrument.
44. Dental Mirror
- Use: For intraoral examination.
- Picture Description: Small round mirror on handle.
45. Periodontal Probe
- Use: Measures gum pocket depth.
- Picture Description: Thin calibrated metal stick.
8. ENT (Ear, Nose, Throat) Instruments
46. Ear Speculum
- Use: Examines ear canal.
- Picture Description: Conical stainless device.
47. Nasal Speculum
- Use: Opens nasal cavity.
- Picture Description: Spring-operated instrument.
48. Laryngoscope
- Use: Views throat and vocal cords.
- Picture Description: Handle with detachable blade.
49. Tongue Depressor
- Use: Holds tongue for examination.
- Picture Description: Flat smooth metal or wood strip.
9. Specialized and Miscellaneous Instruments
50. Suction Tip (Yankauer)
- Use: Removes fluids from surgical area.
- Picture Description: Stainless suction tube.
51. Catheter
- Use: Drains fluids from bladder or wounds.
- Picture Description: Flexible rubber or metal tube.
52. Syringe and Needle
- Use: Injects or withdraws fluids.
- Picture Description: Transparent barrel with stainless needle.
53. Surgical Tray
- Use: Holds sterile instruments.
- Picture Description: Rectangular stainless tray.
54. Sterilization Box
- Use: Stores and sterilizes tools.
- Picture Description: Metal box with vent holes.
Maintenance and Sterilization of Surgical Instruments
Proper care ensures long-lasting performance and safety.
Cleaning:
Immediately rinse after use with distilled water.
Disinfection:
Use enzymatic or ultrasonic cleaning systems.
Sterilization:
Autoclaving (steam under pressure) is the most effective method.
Storage:
Keep dry and sterile in trays or pouches.
Where to Get 54 Basic Surgical Instruments with Pictures
1. Medical Manufacturers
Trusted exporters like Professional Enterprises provide complete catalogs with product codes, names, and photos.
2. Educational Platforms
Medical textbooks and online learning resources show detailed images.
3. Hospitals & Clinics
Institutions maintain sets of labeled surgical tools for staff training.
Why Choose Professional Enterprises
At Professional Enterprises, we manufacture and export premium surgical, dental, and medical instruments worldwide.
Our Key Advantages:
- 100% German stainless steel.
- ISO, CE, and FDA certified.
- Labeled photos, product codes, and packaging.
- Custom branding and OEM service.
- Global delivery at competitive prices.
We provide a complete set of 54 basic surgical instruments with pictures for medical colleges, hospitals, and distributors.
FAQs – 54 Basic Surgical Instruments with Pictures
Q1: Why are pictures important in learning surgical instruments?
Photos help identify instruments easily and prevent confusion in surgeries.
Q2: How can I get a full catalog?
You can request one from Professional Enterprises, complete with pictures, names, and product codes.
Q3: Are all instruments made of stainless steel?
Yes, surgical-grade stainless steel ensures durability and sterilization safety.
Q4: What is the most used surgical instrument?
The scalpel, scissors, and forceps are used in nearly every surgical procedure.
Conclusion
Understanding the 54 basic surgical instruments with pictures is vital for medical students, doctors, and healthcare professionals. Visual learning simplifies identification, ensures surgical precision, and improves clinical performance.
If you’re looking for authentic, high-quality surgical instruments with complete images and product details, Professional Enterprises provides the best range of medical and dental tools — crafted to perfection, tested for reliability, and trusted worldwide.